McGuire, D. K. et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 6, 148–158 (2021).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04564742 (2023).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04509674 (2023).
McDonagh, T. A. et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 42, 3599–3726 (2021).
Heidenreich, P. A. et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 79, 1757–1780 (2022).
UK Kidney Association. UK Kidney Association clinical practice guideline: sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibition in adults with kidney disease.https://ukkidney.org/sites/renal.org/files/UKKA%20guideline_SGLT2i%20in%20adults%20with%20kidney%20disease%20v1%2020.10.21.pdf (2021).
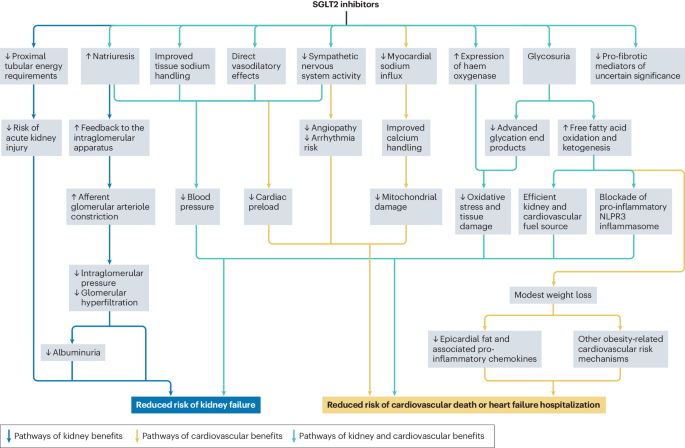
Cowie, M. R. & Fisher, M. SGLT2 inhibitors: mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit beyond glycaemic control. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 17, 761–772 (2020).
Youssef, M. E. et al. Unlocking the full potential of SGLT2 inhibitors: expanding applications beyond glycemic control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 6039 (2023).
Curthoys, N. P. & Moe, O. W. Proximal tubule function and response to acidosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 9, 1627–1638 (2014).
Hou, Y. C., Zheng, C. M., Yen, T. H. & Lu, K. C. Molecular mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitor on cardiorenal protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7833 (2020).
Heerspink, H. J., Perkins, B. A., Fitchett, D. H., Husain, M. & Cherney, D. Z. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation 134, 752–772 (2016).
Cherney, D. Z., Kanbay, M. & Lovshin, J. A. Renal physiology of glucose handling and therapeutic implications. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 35, i3–i12 (2020).
Zaccardi, F. et al. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 18, 783–794 (2016).
DeFronzo, R. A. et al. Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36, 3169–3176 (2013).
Ojima, A., Matsui, T., Nishino, Y., Nakamura, N. & Yamagishi, S. Empagliflozin, an inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 exerts anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects on experimental diabetic nephropathy partly by suppressing AGEs-receptor axis. Horm. Metab. Res. 47, 686–692 (2015).
Yang, L. et al. Dapagliflozin alleviates advanced glycation end product induced podocyte injury through AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway. Cell Signal. 90, 110206 (2022).
Thomas, M. C. & Cherney, D. Z. I. The actions of SGLT2 inhibitors on metabolism, renal function and blood pressure. Diabetologia 61, 2098–2107 (2018).
Cravedi, P. & Remuzzi, G. Pathophysiology of proteinuria and its value as an outcome measure in chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 76, 516–523 (2013).
Karg, M. V. et al. SGLT-2-inhibition with dapagliflozin reduces tissue sodium content: a randomised controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 17, 5 (2018).
Hallow, K. M., Helmlinger, G., Greasley, P. J., McMurray, J. J. V. & Boulton, D. W. Why do SGLT2 inhibitors reduce heart failure hospitalization? A differential volume regulation hypothesis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20, 479–487 (2018).
Uthman, L. et al. Class effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in mouse cardiomyocytes and hearts: inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger, lowering of cytosolic Na(+) and vasodilation. Diabetologia 61, 722–726 (2018).
Trum, M., Riechel, J. & Wagner, S. Cardioprotection by SGLT2 inhibitors-does it all come down to Na+? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7976 (2021).
Peyton, K. J., Behnammanesh, G., Durante, G. L. & Durante, W. Canagliflozin inhibits human endothelial cell inflammation through the induction of heme oxygenase-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 8777 (2022).
Campbell, N. K., Fitzgerald, H. K. & Dunne, A. Regulation of inflammation by the antioxidant haem oxygenase 1. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 21, 411–425 (2021).
Consoli, V., Sorrenti, V., Grosso, S. & Vanella, L. Heme oxygenase-1 signaling and redox homeostasis in physiopathological conditions. Biomolecules 11, 589 (2021).
Gager, G. M. et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on ion homeostasis and oxidative stress associated mechanisms in heart failure. Biomed. Pharmacother. 143, 112169 (2021).
Oraby, M. A., El-Yamany, M. F., Safar, M. M., Assaf, N. & Ghoneim, H. A. Dapagliflozin attenuates early markers of diabetic nephropathy in fructose-streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 109, 910–920 (2019).
Ye, Y., Bajaj, M., Yang, H. C., Perez-Polo, J. R. & Birnbaum, Y. SGLT-2 inhibition with dapagliflozin reduces the activation of the Nlrp3/ASC inflammasome and attenuates the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice with type 2 diabetes. Further augmentation of the effects with saxagliptin, a DPP4 inhibitor. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 31, 119–132 (2017).
Niu, Y. et al. Canagliflozin ameliorates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling and upregulating Bif-1. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 820541 (2022).
Abdollahi, E. et al. Dapagliflozin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of LPS-induced TLR-4 overexpression and NF-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells and differentiated macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 918, 174715 (2022).
Skrabic, R. et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in chronic kidney disease: from mechanisms to clinical practice. Biomedicines 10, 2458 (2022).
Androutsakos, T. et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3107 (2022).
Lupsa, B. C., Kibbey, R. G. & Inzucchi, S. E. Ketones: the double-edged sword of SGLT2 inhibitors? Diabetologia 66, 23–32 (2023).
Ferrannini, E. et al. Shift to fatty substrate utilization in response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in subjects without diabetes and patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 65, 1190–1195 (2016).
Youm, Y. H. et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 21, 263–269 (2015).
Swanson, K. V., Deng, M. & Ting, J. P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19, 477–489 (2019).
Tomita, I. et al. SGLT2 inhibition mediates protection from diabetic kidney disease by promoting ketone body-induced mTORC1 inhibition. Cell Metab. 32, 404–419.e6 (2020).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: a potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 62, 1154–1166 (2019).
Zhang, Y. et al. A sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor attenuates renal capillary injury and fibrosis by a vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent pathway after renal injury in mice. Kidney Int. 94, 524–535 (2018).
Hesp, A. C. et al. The role of renal hypoxia in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease: a promising target for newer renoprotective agents including SGLT2 inhibitors? Kidney Int. 98, 579–589 (2020).
Lauritsen, K. M. et al. SGLT2 inhibition does not affect myocardial fatty acid oxidation or uptake, but reduces myocardial glucose uptake and blood flow in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Diabetes 70, 800–808 (2021).
Gao, Y. M. et al. Cardiorenal protection of SGLT2 inhibitors – perspectives from metabolic reprogramming. EBioMedicine 83, 104215 (2022).
Sano, M. A new class of drugs for heart failure: SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sympathetic overactivity. J. Cardiol. 71, 471–476 (2018).
Sano, M. Sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT)-2 inhibitors alleviate the renal stress responsible for sympathetic activation. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 14, 1753944720939383 (2020).
Scheen, A. J. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on the sympathetic nervous system and blood pressure. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 21, 70 (2019).
Li, T., Chen, Y., Gua, C. & Wu, B. Elevated oxidative stress and inflammation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus are associated with sympathetic excitation and hypertension in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 9, 840 (2018).
Ye, S., Zhong, H., Yanamadala, S. & Campese, V. M. Oxidative stress mediates the stimulation of sympathetic nerve activity in the phenol renal injury model of hypertension. Hypertension 48, 309–315 (2006).
Manosroi, W., Danpanichkul, P. & Atthakomol, P. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on aldosterone and renin levels in diabetes mellitus type 2 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 12, 19603 (2022).
Seidu, S., Kunutsor, S. K., Topsever, P. & Khunti, K. Benefits and harms of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2-I) and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors (RAAS-I) versus SGLT2-Is alone in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 5, e00303 (2022).
Neuen, B. L. et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 7, 845–854 (2019).
Iacobellis, G. & Gra-Menendez, S. Effects of dapagliflozin on epicardial fat thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Obesity 28, 1068–1074 (2020).
Camarena, V. et al. Novel atherogenic pathways from the differential transcriptome analysis of diabetic epicardial adipose tissue. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 27, 739–750 (2017).
Díaz-Rodríguez, E. et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on human epicardial adipose tissue: modulation of insulin resistance, inflammatory chemokine production, and differentiation ability. Cardiovasc. Res. 114, 336–346 (2018).
Durante, W., Behnammanesh, G. & Peyton, K. J. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on vascular cell function and arterial remodeling. Int J. Mol. Sci. 22, 8786 (2021).
Lescano, C. H. et al. The sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors synergize with nitric oxide and prostacyclin to reduce human platelet activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 182, 114276 (2020).
Dhingra, N. K. et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and cardiac remodelling: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized cardiac magnetic resonance imaging trials. ESC Heart Fail. 8, 4693–4700 (2021).
Herrington, W. G. et al. Cardiac, renal, and metabolic effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: a position paper from the European Society of Cardiology ad-hoc task force on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 23, 1260–1275 (2021).
Cefalu, W. T. et al. Cardiovascular outcomes trials in type 2 diabetes: where do we go from here? Reflections from a diabetes care editors’ expert forum. Diabetes Care 41, 14–31 (2018).
Zinman, B. et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 2117–2128 (2015).
Wanner, C. et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Eng. J. Med. 375, 323–334 (2016).
Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group. SGLT2 inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 400, 1788–1801 (2022).
Perkovic, V. et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 380, 2295–2306 (2019).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1436–1446 (2020).
Herrington, W. G. et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 117–127 (2023).
Packer, M. et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1413–1424 (2020).
McMurray, J. J. V. et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 1995–2008 (2019).
Anker, S. D. et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 1451–1461 (2021).
Solomon, S. D. et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 387, 1089–1098 (2022).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05374291 (2023).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03819153 (2024).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05254002 (2024).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Change in albuminuria as a surrogate endpoint for progression of kidney disease: a meta-analysis of treatment effects in randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 7, 128–139 (2019).
Heerspink, H. J. et al. Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independently of glycemic effects. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 368–375 (2017).
Neal, B. et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Eng. J. Med. 377, 644–657 (2017).
Wiviott, S. D. et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Eng. J. Med. 380, 347–357 (2019).
Cannon, C. P. et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1425–1435 (2020).
Bhatt, D. L. et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 129–139 (2020).
Mosenzon, O. et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on development and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 7, 606–617 (2019).
Persson, F. et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin by baseline glycemic status: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Diabetes Care 44, 1894–1897 (2021).
Afsar, B. et al. Sodium–glucose cotransporter inhibition in polycystic kidney disease: fact or fiction. Clin. Kidney J. 15, 1275–1283 (2022).
Ujjawal, A., Schreiber, B. & Verma, A. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) in kidney transplant recipients: what is the evidence? Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 20420188221090001 (2022).
Neuen, B. L. et al. Effect of canagliflozin on renal and cardiovascular outcomes across different levels of albuminuria: data from the CANVAS Program. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 30, 2229–2242 (2019).
Jardine, M. et al. Kidney, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes of canagliflozin according to baseline albuminuria: a CREDENCE secondary analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 384–395 (2021).
Heerspink, H. J. L. et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on the rate of decline in kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9, 743–754 (2021).
Inker, L. A. et al. A meta-analysis of GFR slope as a surrogate endpoint for kidney failure. Nat. Med. 29, 1867–1876 (2023).
Kraus, B. J. et al. Characterization and implications of the initial estimated glomerular filtration rate ‘dip’ upon sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition with empagliflozin in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Kidney Int. 99, 750–762 (2021).
Jongs, N. et al. Correlates and consequences of an acute change in eGFR in response to the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 33, 2094–2107 (2022).
Sridhar, V. S., Tuttle, K. R. & Cherney, D. Z. I. We can finally stop worrying about SGLT2 inhibitors and acute kidney injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 76, 454–456 (2020).
Neuen, B. L. et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of hyperkalemia in people with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomized, controlled trials. Circulation 145, 1460–1470 (2022).
Charlwood, C., Chudasama, J., Darling, A. L., Logan Ellis, H. & Whyte, M. B. Effect of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on plasma potassium: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 196, 110239 (2023).
Halden, T. A. S. et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in renal transplant recipients with posttransplant diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 42, 1067–1074 (2019).
Oliveras, L., Montero, N. & Cruzado, J. M. Searching in the maze: sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients to improve survival. Clin. Kidney J. 16, 909–913 (2023).
Maffei, P., Bettini, S., Busetto, L. & Dassie, F. SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of type 1 diabetes (T1D): an update on current evidence and recommendations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 16, 3579–3598 (2023).
Inzucchi, S. E. et al. Improvement in cardiovascular outcomes with empagliflozin is independent of glycemic control. Circulation 138, 1904–1907 (2018).
Inzucchi, S. E. et al. Cardiovascular benefit of empagliflozin across the spectrum of cardiovascular risk factor control in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 105, 3025–3035 (2020).
Tsai, P. C. et al. Neutral effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in acute coronary syndromes, peripheral arterial occlusive disease, or ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 22, 57 (2023).
Sattar, N. et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9, 653–662 (2021).
Lam, C. S. P. et al. Efpeglenatide and clinical outcomes with and without concomitant sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition use in type 2 diabetes: exploratory analysis of the AMPLITUDE-O trial. Circulation 145, 565–574 (2022).
Pitt, B. & Bhatt, D. L. Does SGLT1 inhibition add benefit to SGLT2 inhibition in type 2 diabetes? Circulation 144, 4–6 (2021).
Zannad, F. et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a meta-analysis of the EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF trials. Lancet 396, 819–829 (2020).
Butler, J. et al. Empagliflozin and health-related quality of life outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the EMPEROR-Reduced trial. Eur. Heart J. 42, 1203–1212 (2021).
Vaduganathan, M. et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure: a comprehensive meta-analysis of five randomised controlled trials. Lancet 400, 757–767 (2022).
Butler, J. et al. Empagliflozin, health status, and quality of life in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: the EMPEROR-Preserved trial. Circulation 145, 184–193 (2022).
Kosiborod, M. N. et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on health status in patients with preserved or mildly reduced ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 81, 460–473 (2023).
McDonagh, T. A. et al. 2023 focused update of the 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 44, 3627–3639 (2023).
Voors, A. A. et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: a multinational randomized trial. Nat. Med. 28, 568–574 (2022).
Bhatt, D. L. et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 117–128 (2021).
Berg, D. D. et al. Time to clinical benefit of dapagliflozin and significance of prior heart failure hospitalization in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 6, 499–507 (2021).
Vaduganathan, M. et al. Time to clinical benefit of dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction: a prespecified secondary analysis of the DELIVER randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 7, 1259–1263 (2022).
Provenzano, M. et al. POS-255 Effect of dapagliflozin on blood pressure in patients with CKD: a pre-specified analysis from DAPA-CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 7, S112 (2022).
Ye, N. et al. Blood pressure effects of canagliflozin and clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Circulation 143, 1735–1749 (2021).
Del Prato, S. et al. Long-term glycaemic response and tolerability of dapagliflozin versus a sulphonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4-year data. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 17, 581–590 (2015).
Cheong, A. J. Y. et al. SGLT inhibitors on weight and body mass: a meta-analysis of 116 randomized-controlled trials. Obesity 30, 117–128 (2022).
Cai, X. et al. The association between the dosage of SGLT2 inhibitor and weight reduction in type 2 diabetes patients: a meta-analysis. Obesity 26, 70–80 (2018).
Inzucchi, S. E. et al. Empagliflozin treatment effects across categories of baseline HbA1c, body weight and blood pressure as an add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 23, 425–433 (2021).
Pan, R. et al. Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 17, e0279889 (2022).
Cefalu, W. T. et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA-SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 382, 941–950 (2013).
Ridderstrale, M. et al. Comparison of empagliflozin and glimepiride as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 104-week randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2, 691–700 (2014).
Ferrannini, G. et al. Energy balance after sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Care 38, 1730–1735 (2015).
Mayne, K. J. et al. Effects of empagliflozin on fluid overload, weight and blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 35, 202–215 (2023).
Hollander, P. et al. Coadministration of canagliflozin and phentermine for weight management in overweight and obese individuals without diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 40, 632–639 (2017).
Frias, J. P. et al. Exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin once daily versus exenatide or dapagliflozin alone in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy (DURATION-8): a 28 week, multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 4, 1004–1016 (2016).
Li, C., Luo, J., Jiang, M. & Wang, K. The efficacy and safety of the combination therapy with GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 838277 (2022).
Lundkvist, P. et al. Dapagliflozin once daily plus exenatide once weekly in obese adults without diabetes: sustained reductions in body weight, glycaemia and blood pressure over 1 year. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 19, 1276–1288 (2017).
Rinella, M. E. et al. A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 78, 1966–1986 (2023).
Dufour, J. F. et al. Current therapies and new developments in NASH. Gut 71, 2123–2134 (2022).
Sinha, B., Datta, D. & Ghosal, S. Meta-analysis of the effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with type 2 diabetes. JGH Open 5, 219–227 (2021).
Shao, S. C., Kuo, L. T., Chien, R. N., Hung, M. J. & Lai, E. C. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases: an umbrella review of systematic reviews. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 8, e001956 (2020).
Xing, B. et al. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes Investig. 11, 1238–1247 (2020).
Wei, Q., Xu, X., Guo, L., Li, J. & Li, L. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on type 2 diabetes mellitus with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 635556 (2021).
Wong, C. et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 11, 609135 (2020).
Taheri, H. et al. Effect of empagliflozin on liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Adv. Ther. 37, 4697–4708 (2020).
Tobita, H. et al. Comparison of dapagliflozin and teneligliptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus: a prospective randomized study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 68, 173–180 (2021).
Spiazzi, B. F. et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and cancer outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 198, 110621 (2023).
Kohler, S., Lee, J., George, J. T., Inzucchi, S. E. & Zinman, B. Bladder cancer in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetologia 60, 2534–2535 (2017).
Tang, H. et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 60, 1862–1872 (2017).
Abrahami, D. et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and the short-term risk of bladder cancer: an international multisite cohort study. Diabetes Care 45, 2907–2917 (2022).
Hu, W. S. & Lin, C. L. Patients with diabetes with and without sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors use with incident cancer risk. J. Diabetes Complications 37, 108468 (2023).
Wu, W. et al. SGLT2 inhibitor activates the STING/IRF3/IFN-β pathway and induces immune infiltration in osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 13, 523 (2022).
Wang, Y. et al. SGLT2 inhibition restrains thyroid cancer growth via G1/S phase transition arrest and apoptosis mediated by DNA damage response signaling pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 22, 74 (2022).
Jiang, D. & Ma, P. Canagliflozin, characterized as a HDAC6 inhibitor, inhibits gastric cancer metastasis. Front. Oncol. 12, 1057455 (2022).
Dutka, M. et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in cancer treatment – mechanisms of action and emerging new perspectives. Cancers 14, 5811 (2022).
Schietzel, S. et al. Impact of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin on urinary supersaturations in kidney stone formers (SWEETSTONE trial): protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. BMJ Open 12, e059073 (2022).
Balasubramanian, P. et al. Empagliflozin and decreased risk of nephrolithiasis: a potential new role for SGLT2 inhibition? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 107, e3003–e3007 (2022).
Bailey, C. J. Uric acid and the cardio-renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 21, 1291–1298 (2019).
Banerjee, M., Pal, R., Maisnam, I., Chowdhury, S. & Mukhopadhyay, S. Serum uric acid lowering and effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on gout: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 25, 2697–2703 (2023).
Packer, M. Alleviation of anemia by SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with CKD: mechanisms and results of long-term placebo-controlled trials. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.0000000000000362 (2023).
Singh, D. K., Winocour, P. & Farrington, K. Erythropoietic stress and anemia in diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 5, 204–210 (2009).
Okunrintemi, V., Mishriky, B. M., Powell, J. R. & Cummings, D. M. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and atrial fibrillation in the cardiovascular and renal outcome trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 23, 276–280 (2021).
O’Hara, D. V. & Jardine, M. J. SGLT2 inhibitors may prevent diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 203–204 (2022).
Kosiborod, M. N. et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with cardiometabolic risk factors hospitalised with COVID-19 (DARE-19): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9, 586–594 (2021).
The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Empagliflozin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 11, 905–914 (2023).
ESC Press Office. SGLT2 inhibitors not linked with improved survival in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: SGLT2 inhibitors in COVID-19 meta-analysis presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023 European Society of Cardiology https://www.escardio.org/The-ESC/Press-Office/Press-releases/SGLT2-inhibitors-not-linked-with-improved-survival-in-hospitalised-COVID-19-patients (2023).
Thiruvenkatarajan, V. et al. Peri-colonoscopy implications of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor therapy: a mini-review of available evidence. Can. J. Diabetes 47, 287–291 (2023).
Khunti, K. et al. Re-examining the widespread policy of stopping sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors during acute illness: a perspective based on the updated evidence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 24, 2071–2080 (2022).
Raven, L. M., Muir, C. A. & Greenfield, J. R. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor-induced ketoacidosis is unlikely in patients without diabetes. Med. J. Aust. 219, 293–294 (2023).
Hayes, A. G., Raven, L. M., Viardot, A., Kotlyar, E. & Greenfield, J. R. SGLT2 inhibitor-induced ketoacidosis in a patient without diabetes. Diabetes Care 47, e4–e5 (2024).
Duggan, A., Stewart, P. & Williams, D. Non-diabetic euglycaemic ketoacidosis secondary to SGLT2 inhibition. Heart Lung Circ. 32, S167–S168 (2023).
Vukadinović, D. et al. Side effects and treatment initiation barriers of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 24, 1625–1632 (2022).
Jardine, M. J. et al. Renal, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes of canagliflozin by baseline kidney function: a secondary analysis of the CREDENCE randomized trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 31, 1128–1139 (2020).
Neuen, B. L., Jardine, M. J. & Perkovic, V. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition: which patient with chronic kidney disease should be treated in the future? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 35, i48–i55 (2020).
Li, C. X. et al. Comparative safety of different sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1238399 (2023).
Kang, A. et al. P1013. Canagliflozin and risk of genital infections and urinary tract infections in people with diabetes mellitus and kidney disease – a post-hoc analysis of the CREDENCE trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 35, gfaa142 (2020).
Engelhardt, K., Ferguson, M. & Rosselli, J. L. Prevention and management of genital mycotic infections in the setting of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Ann. Pharmacother. 55, 543–548 (2021).
Liu, J. et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on UTIs and genital infections in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 7, 2824 (2017).
Butt, J. H. et al. Heart failure, peripheral artery disease, and dapagliflozin: a patient-level meta-analysis of DAPA-HF and DELIVER. Eur. Heart J. 44, 2170–2183 (2023).
Fralick, M. et al. Fracture risk after initiation of use of canagliflozin: a cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 170, 155–163 (2019).
Patil, T., Cook, M., Hobson, J., Kaur, A. & Lee, A. Evaluating the safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in a nationwide Veterans Health Administration observational cohort study. Am. J. Cardiol. 201, 281–293 (2023).
McEwan, P. et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin as a treatment for chronic kidney disease: a health-economic analysis of DAPA-CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 1730–1741 (2022).
Igarashi, A. et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of initiating type 2 diabetes therapy with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor versus conventional therapy in Japan. Diabetes Ther. 13, 1367–1381 (2022).
Johnston, R. et al. Canagliflozin, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin monotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 21, 1–218 (2017).
Sabapathy, S. et al. Cost-effectiveness of canagliflozin versus sitagliptin when added to metformin and sulfonylurea in type 2 diabetes in Canada. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 23, e151–e168 (2016).
Gourzoulidis, G. et al. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at increased cardiovascular risk in Greece. Clin. Drug Investig. 38, 417–426 (2018).
Nguyen, E., Coleman, C. I., Nair, S. & Weeda, E. R. Cost-utility of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk. J. Diabetes Complications 32, 210–215 (2018).
Mettam, S. R., Bajaj, H., Kansal, A. R. & Kandaswamy, P. Cost effectiveness of empagliflozin in patients with T2DM and high CV risk in Canada. Value Health 19, A674 (2016).
Daacke, I., Kandaswamy, P., Tebboth, A., Kansal, A. & Reifsnider, O. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin (Jardiance) in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the UK based on EMPA-REG-OUTCOME data. Value Health 19, A673 (2016).
Reifsnider, O. S. et al. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin in patients with diabetic kidney disease in the United States: findings based on the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 79, 796–806 (2022).
Jorissen, W., Annemans, L., Louis, N., Nilsson, A. & Willis, M. Health economic modelling of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with canagliflozin in Belgium. Acta Clin. Belg. 77, 945–954 (2022).
Willis, M. et al. Cost-effectiveness of canagliflozin added to standard of care for treating diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in England: estimates using the CREDEM-DKD model. Diabetes Ther. 12, 313–328 (2021).
Tisdale, R. L. et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 37, 3380–3387 (2022).
Kodera, S. et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for chronic kidney disease in Japan. Circ. J. 86, 2021–2028 (2022).
Vareesangthip, K., Deerochanawong, C., Thongsuk, D., Pojchaijongdee, N. & Permsuwan, U. Cost-utility analysis of dapagliflozin as an add-on to standard of care for patients with chronic kidney disease in Thailand. Adv. Ther. 39, 1279–1292 (2022).
Lim, A. H., Abdul Rahim, N., Zhao, J., Cheung, S. Y. A. & Lin, Y. W. Cost effectiveness analyses of pharmacological treatments in heart failure. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 919974 (2022).
Gil-Rojas, Y., Lasalvia, P. & García, Á. Cost-utility of dapagliflozin plus standard treatment compared to standard treatment for the management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in Colombia. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 22, 655–663 (2022).
Isaza, N. et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. JAMA Netw. Open 4, e2114501 (2021).
Krittayaphong, R. & Permsuwan, U. Cost-utility analysis of add-on dapagliflozin treatment in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 322, 183–190 (2021).
& Liao, C.-T. et al. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of add-on empagliflozin in patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction from the healthcare system’s perspective in the Asia–Pacific Region. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 750381 (2021).
Liao, C.-T. et al. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of add-on dapagliflozin for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction from perspective of healthcare systems in Asia–Pacific region. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 20, 204 (2021).
Mohammadnezhad, G., Azadmehr, B., Mirheidari, M. & Yousefi, N. Cost-effectiveness analysis of dapagliflozin in the management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): a systematic review. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 20, 62 (2022).
Nguyen, B. N., Mital, S., Bugden, S. & Nguyen, H. V. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin and empagliflozin for treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 376, 83–89 (2023).
Parizo, J. T. et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for treatment of patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 6, 926–935 (2021).
Reifsnider, O. S. et al. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin in the UK in an EMPA-REG OUTCOME subgroup with type 2 diabetes and heart failure. Esc. Heart Fail. 7, 3910–3918 (2020).
Sang, H., Wan, Y., Ma, Z., Zhang, S. & Zhao, Q. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in China. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9, 1022020 (2022).
Cohen, L. P. et al. Cost-effectiveness of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 8, 419–428 (2023).
Global Health & Population Project on Access to Care for Cardiometabolic Diseases Expanding access to newer medicines for people with type 2 diabetes in low-income and middle-income countries: a cost-effectiveness and price target analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9, 825–836 (2021).
The George Institute. The wider benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors. Health TGIfG. https://www.georgeinstitute.org.au/our-impact/policy-and-recommendations/the-wider-benefits-of-sglt2-inhibitors 2021.
Mosenzon, O. et al. CAPTURE: a multinational, cross-sectional study of cardiovascular disease prevalence in adults with type 2 diabetes across 13 countries. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 20, 154 (2021).
Arnold, S. V. et al. Global use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes. Results from DISCOVER. BMC Endocr. Disord. 22, 111 (2022).
Nargesi, A. A. et al. Contemporary national patterns of eligibility and use of novel cardioprotective antihyperglycemic agents in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10, e021084 (2021).
Gay, H. C. et al. Comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist prescribing in patients with diabetes mellitus with and without cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 189, 121–130 (2023).
Ofori-Asenso, R. et al. Poor adherence and persistence to sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in real-world settings: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 37, e3350 (2021).
Luo, J. et al. Incidence and predictors of primary nonadherence to sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists in a large integrated healthcare system. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 37, 3562–3569 (2022).
Vardeny, O. & Vaduganathan, M. Practical guide to prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for cardiologists. JACC: Heart Fail. 7, 169–172 (2019).
Essien, U. R. et al. Association of prescription co-payment with adherence to glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor therapies in patients with heart failure and diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 6, e2316290 (2023).
- The Renal Warrior Project. Join Now
- Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-024-00836-y
